Automation of manual tasks and processes
Automating manual tasks related to business processes, customer services, or manufacturing is a clear-cut benefit. The idea is not to reduce personnel but rather to reduce the handling of repetitive, time-consuming tasks so that professionals are free to focus on higher-value tasks.
Let’s consider the example of processing an application for a credit card or a loan. In this scenario, the customer submits an application which the bank personnel must enter into the bank systems, review, verify and calculate the risk score. By relying on AI technology to perform these tasks, financial institutions can reduce the time needed to approve an application and increase the accuracy by avoiding human errors and minimizing the related risks.
Santander Consumer Multirent, a leading financial institution being part of the larger Santander Spanish Group, developed a fully automated digital leasing process. Customers can submit a car lease request, verify their identity through mobile phone thanks to facial recognition techniques, calculate their credit scoring and perform a risk assessment to process the request quickly and efficiently.
Identification and fraud prevention
In today’s digitalized world, fraudsters and fraud rings continue to become more sophisticated, making fraud protection and detection much harder. With all these complexities and the amount of transaction data growing exponentially, humans are just not capable of quickly identifying suspicious behaviours and picking fraud transactions buried in millions of legitimate ones.
The first benefit of using AI for fraud prevention is that the whole process becomes much quicker and cost-effective. Also, AI improves accuracy by significantly reducing false positives and false negatives.
As for fraud detection, an AI model is trained on large amounts of data – both static customer information and dynamic transaction data – to recognize suspicious behaviours and patterns and identify irregular events. Humans don’t need to waste hours processing and analyzing millions of transactions.
A well-designed AI system is constantly developed through ongoing model training with new data and classifications, making it smarter over time. As a result, AI does an exceptionally better job of correctly identifying abnormal behaviour than any human could. Therefore, it helps organizations reduce fraud risk and costs, all while enhancing customer satisfaction.
PZU, a large insurance provider based in central Europe, has developed the ability to identify fraudulent medical claims. Using AI/ML models applied to Big Data (a tenth of millions of records were tested), PZU resulted in a 5M Euro reduction in their cost by detecting thousands of monthly fraudulent medical claims. 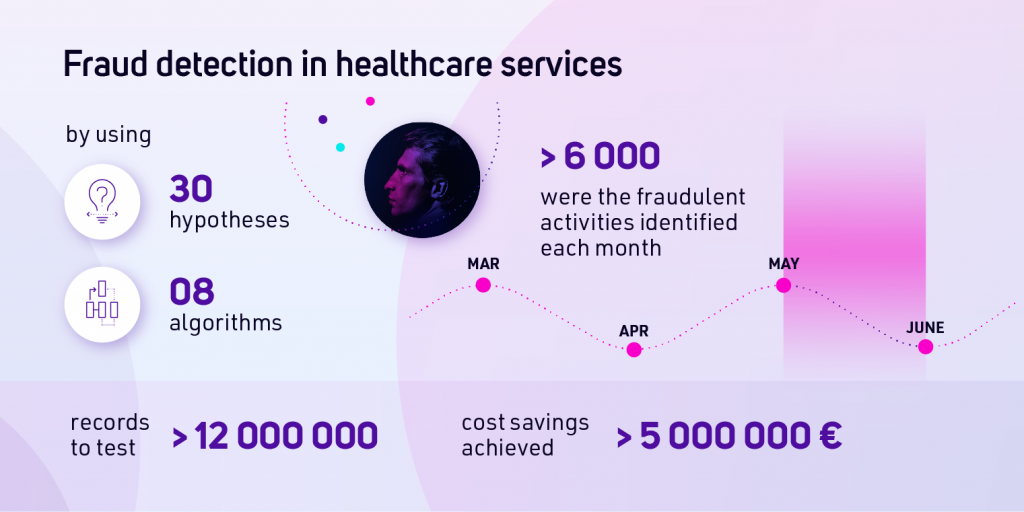
Better customer experience and cost reduction
AI can also be used to provide a more personalized and efficient experience to customers.
For instance, AI-powered chatbots (also called Digital Assistants to distinguish them from simple, plug&play and semi-scripted chatbots) can:
- Provide a meaningful and natural conversation with the customer by leveraging Natural Language Processing as well as Speech-to-Text and Text-to-Speech capabilities.
- Help offer more customized recommendations based on the in-depth analysis of customers’ personal, behavioural, and transactional data, including third party data.
- Utilize multiple data sources to provide a truly multichannel experience and deliver services through different channels.
- Assist customers in completing application forms and supporting them in performing operational tasks while connecting with a human operator with the right skill to assist the customer when required.
For Telecom operators and Financial institutions with large call centres dealing with millions of customers and offering hundreds of products, Digital Assistants can offer substantial help in offloading the call centre and improving customer engagement.
For example, a major European insurance company has achieved a decrease of 80% in the number of interactions with the consultants by implementing a Digital Assistant solution capable of handling damage reporting, claims and policies procedures and activation of new products.
Companies like Omantel, Oman’s Ministry of Health, or Generali have successfully deployed Digital Assistants on several channels. As a result, they obtained substantial operational savings by decreasing up to 80% of the number of interactions with the consultants on the chat and reducing by 15% the consultant’s daily working hours.
Simplification of business decisions
Applying AI and ML to structured and unstructured data gathered from different sources allows companies to unleash their value by extracting insights that can support business decisions.
For example, a large Polish corporate bank obtained 45 different customer segments by analyzing multiple data sources, using thousands of variables, and applying hundreds of ML models – each of the segments with its propensity to buy evaluation. As a result, they could map their product portfolio to the most appropriate segment and create value propositions matching the characteristics of each segment. This resulted in a double-digit increase in their revenue.
A similar method used in an MEA Telco for their prepaid mobile customer bore similar results in selling a specific product that the company had planned to push. 
Conclusions
All these use cases are examples of how AI can support humankind to minimize manual effort and capitalize on human creativity, skills, and intellect across the enterprise. In this scenario, AI empowers human intelligence rather than replacing it.
At the same time, AI can unleash the ability to extract valuable insights from multiple data sources supporting sound business practices and decisions.