Definition and Key Features of Agentic AI
AI Agents are an extended version of chatbots that can not only respond to user queries but can also act independently on behalf of a specific user or system to perform assigned tasks. They can organize workflows and coordinate the tasks of multiple agents. Unlike traditional generative models, they are designed to make decisions and carry out complex actions – often without human intervention.
Due to their autonomy, they are becoming active participants in business processes, and it’s not surprising that as many as 81% of organizations predict that AI agents will be moderately or extensively integrated into their AI strategy within 12–18 months. (Source: 2025: The Year the Frontier Firm Is Born, Microsoft).
A huge advantage of Agentic Artificial Intelligence is that agents learn from previous experiences. This allows them to become better at the tasks they perform, and companies can use them to automate internal processes and increase employee efficiency.
Types of AI Agents
Agentic AI is not a single, universal technology. Depending on the role, skills, or expected results, we can divide them into several main categories:
- Individual user support agents (“copilot”): i.e., personal assistants that support the productivity and capabilities of a specific user.
- Process and task automation platforms: these are agents focused on performing tasks within selected processes. They act like intelligent operators who coordinate and execute tasks according to established rules.
- AI agents for specific business areas: i.e., “AI-native” solutions designed for specific functions, e.g., customer service or software development. Unlike classic tools with an added AI layer, they use artificial intelligence as the foundation of the entire solution.
- Virtual AI employees: as the name suggests, these are agents that work just like real team members. They are able to perform tasks, make decisions, and communicate with other agents, operating within existing organizational structures. Additionally, they enable rapid AI implementation in companies without the need to overhaul the entire organization.
How does Agentic AI differ from traditional and Generative AI?
Traditional AI focuses on performing strictly defined tasks and making decisions based on predefined rules and analysis of existing data. Generative AI expands these capabilities by specializing in creating new, original content – such as text, images, or code – based on patterns learned from vast datasets. In turn, agentic AI represents the most advanced paradigm, where systems are characterized by high autonomy: they independently perceive their environment, plan, make decisions, and perform complex actions to achieve set goals, and may use generative AI as a tool, but their essence is proactive and adaptive interaction with the world. 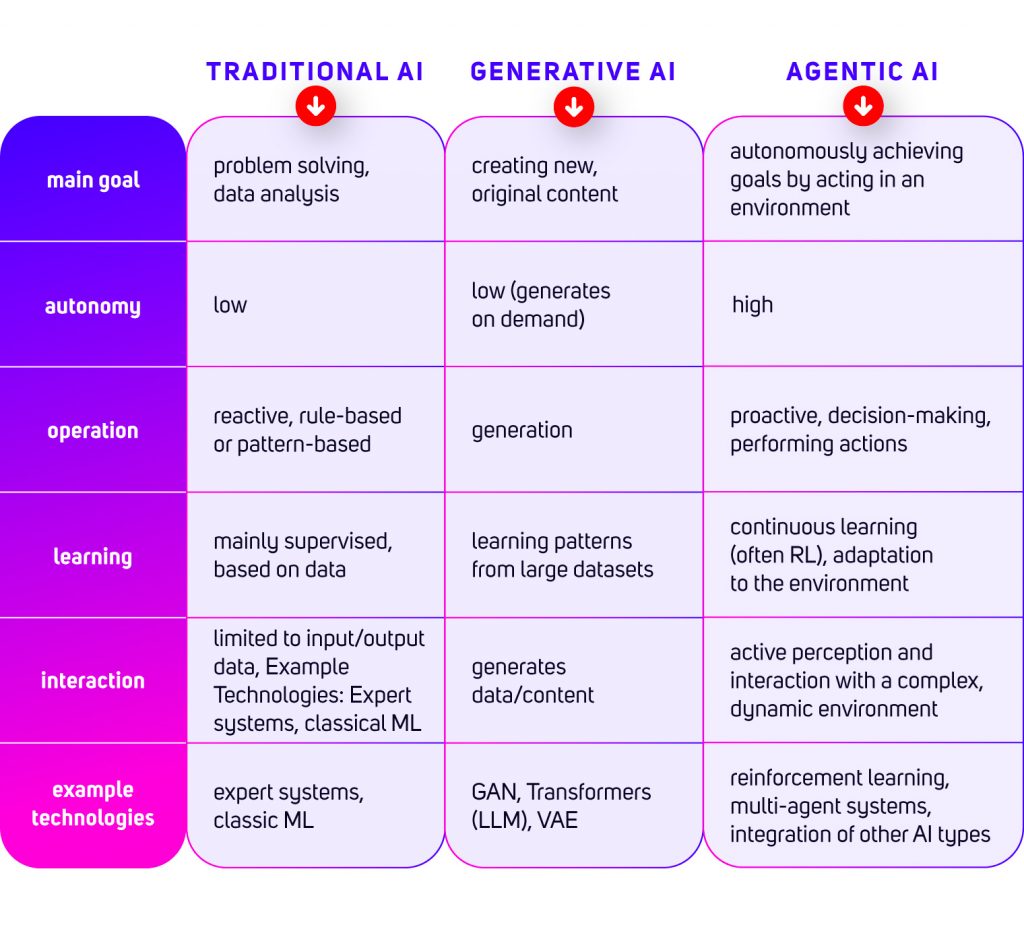
How Agentic AI Works: The Perceive–Reason–Act–Learn Cycle
Agentic AI operates based on a cyclical process that allows it to autonomously interact with its environment and strive to achieve its set goals. This fundamental cycle is often described as Perceive–Reason–Act–Learn. Each of these stages is crucial for the agent’s intelligent and adaptive behavior. 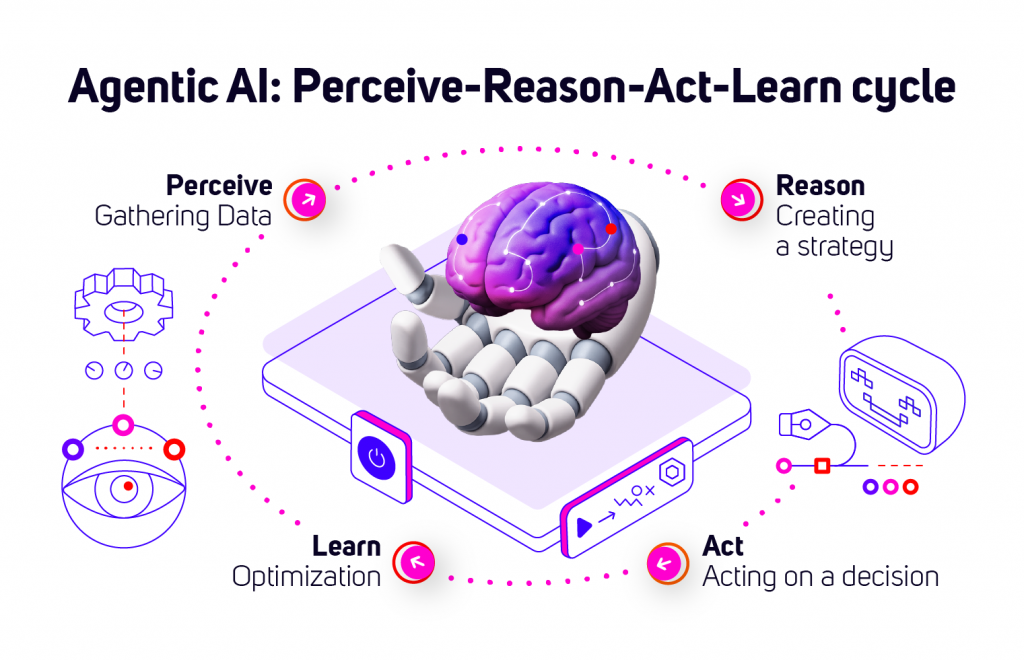
- Perceive: Gathering Information About the World
This is the first step, in which the agent collects data about its current state and the state of its surrounding environment. The environment can be physical (as in robots) or virtual (as in software agents operating on the internet or computer systems). The goal of this stage is to build the most accurate model of the current situation (so-called “situational awareness”), which will serve as the basis for further reasoning and decision-making. The agent must filter out noise and select relevant information.
- Reason: Processing Information and Planning
After collecting data, the agent must interpret it, understand it, and use it to decide what to do next. This stage involves complex cognitive processes. Generating an action plan or selecting a specific action that the agent deems optimal in the context of its goals and current knowledge of the world.
- Act – Influencing the Environment
At this stage, the agent performs the action selected in the reasoning process, thereby influencing its environment or its internal state. The goal is to change the state of the environment (or its own) in a way that brings the agent closer to achieving its goals. Actions are concrete, observable operations.
- Learn – Adaptation and Improvement
This is a key stage that enables the agent to adapt and improve its performance over time. The agent analyzes the results of its actions and uses this information to modify its internal knowledge, models, or strategies. Thanks to this, the agent becomes increasingly effective and intelligent in achieving goals. Through learning, it can cope with new, unforeseen situations and optimize its behavior.
The Perceive–Reason–Act–Learn cycle is not a one-time process but a continuous loop. After performing an action and (potentially) learning something new, the agent returns to the perception stage, collecting updated information about the new state of the environment, and the whole process starts anew. This iterative nature allows the agent to dynamically react to changes, correct errors, and gradually improve its performance.
The Role of AI Agents in Achieving Tasks and Goals in Business
According to McKinsey estimates, agentic AI (agent-based artificial intelligence) has the potential to become a key catalyst for transformation in enterprises, enabling them not only to automate tasks but to fundamentally rethink processes and modernize IT infrastructure. Companies are already beginning to use AI agents in a wide range of applications, leading to significant changes in how they operate and deliver value. 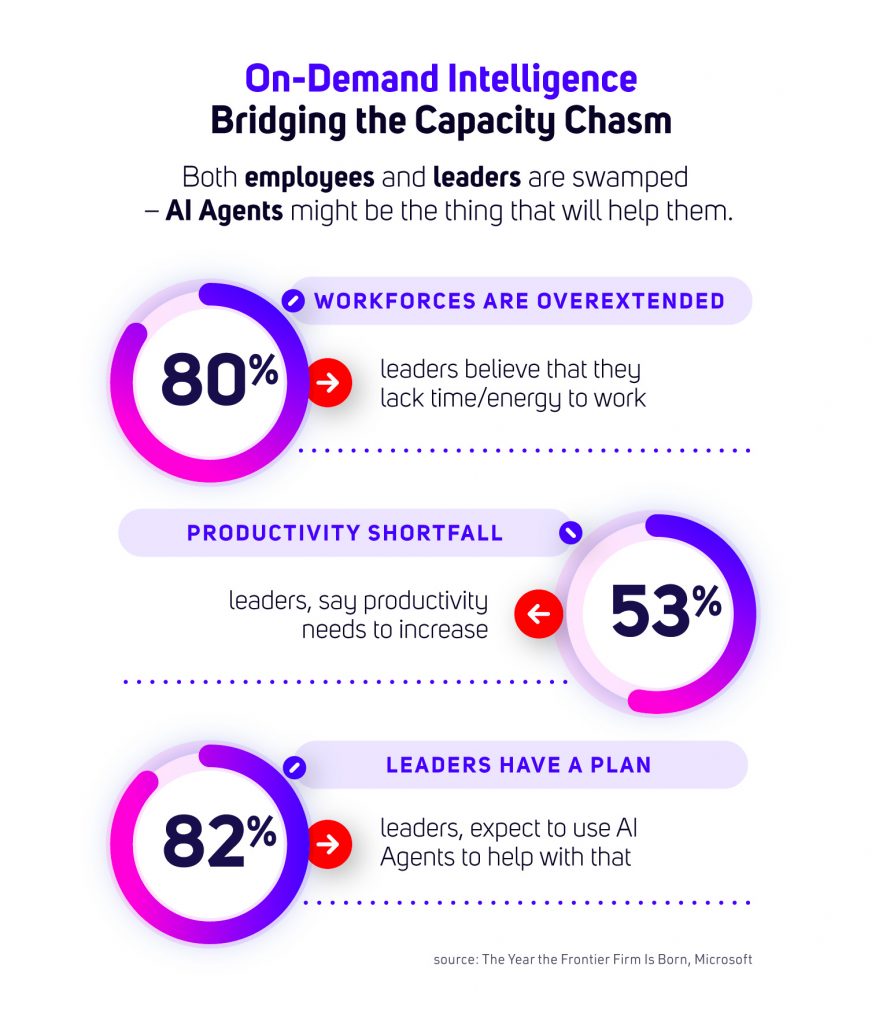
Companies are implementing AI agents to revolutionize their operations on multiple levels:
Automation and Optimization of Complex Processes:
- Customer Service: AI agents autonomously handle complex customer inquiries, solve problems in real-time, and personalize interactions, often without human intervention. An example could be advanced chatbots that not only answer questions but proactively guide the customer through processes, e.g., complaints or configurations.
- Sales and Marketing: They create and manage personalized marketing campaigns, analyze market trends, automate sales activities (e.g., lead generation, follow-ups), and even make dynamic pricing decisions. In e-commerce, the concept of “Agentic Web” is emerging, where AI agents make purchases on behalf of users, comparing offers and negotiating terms.
- Production and Logistics: Intelligent agents monitor production lines, predict equipment failures (predictive maintenance), optimize machine operating parameters, manage inventory in real-time (forecasting demand and automating orders), and plan optimal delivery routes.
- Finance and Risk: They are used for advanced fraud detection, automation of underwriting processes (e.g., credit risk assessment, shortening analysis preparation time), personalized financial advisory, and making automated trading decisions in financial markets.
Rethinking Business Processes:
- From Reactivity to Proactivity: Agentic AI allows companies to move from a model of reacting to events to proactively anticipating needs (e.g., of customers, the market) and taking preventive or optimizing actions.
- Hyper-personalization: The ability to deliver mass-personalized products, services, and experiences tailored to the individual preferences and context of each customer.
- Democratization of Competencies: Thanks to natural language-based interfaces, AI agents enable a wider group of employees, not just IT specialists, to use advanced analytical and automation tools, leading to the creation of new roles and human-AI collaboration models.
- New Business Models: Agentic AI can lead to the redefinition of value chains (e.g., by eliminating intermediaries), the creation of new data-driven services (e.g., “Algorithm-as-a-Service”), and a fundamental change in how companies interact with their customers and partners.
Modernization of IT Infrastructure:
- Automation of IT Tasks: AI agents are used to automate complex IT tasks, such as migrating and modernizing legacy systems and applications, managing cloud infrastructure, testing software, and even writing code. Tools like AWS Transform or McKinsey’s LegacyX demonstrate the potential to significantly accelerate these processes.
- Data and System Integration: They facilitate the integration of distributed data sources (both structured and unstructured) and communication between different systems and platforms, creating more coherent and intelligent IT ecosystems.
- AI Lifecycle Management: The implementation of AI agents forces organizations to develop new competencies and processes related to managing AI models, their versioning, monitoring performance, and ensuring security and compliance with regulations.
- Support for Developers and Analysts: Agents can act as intelligent assistants for IT teams, helping with data analysis, information synthesis, hypothesis testing, and code optimization.
An AI agent for customer service could do more than just answer questions. With agentic artificial intelligence, it could check a user’s outstanding balance and recommend which accounts could be used to pay it off — while waiting for the user’s decision to execute the transaction upon receiving the command. Eric Pounds, Nvidia
Time for the Autonomous Revolution — Elevate Your Organization to the Next Level
Agentic artificial intelligence is not a futuristic vision, but a technology that is already redefining the rules of the game in business. We stand at the threshold of a new era where autonomous systems will make complex decisions, optimize processes, and create value in ways previously unattainable. It’s no longer a question of if, but when and how to harness this potential.
However, to fully leverage the opportunities offered by Agentic AI, it requires not only an understanding of the technology but also strategic partnership and expert knowledge. At TUATARA, we specialize in transforming the potential of artificial intelligence into real business benefits. Our team will help you identify areas where AI agents can bring the greatest value, design and implement tailor-made solutions, and integrate them with your existing infrastructure.
Are you ready to embark on the path of transformation and use agentic artificial intelligence to build a competitive advantage and revolutionize your operations?