What is Cognitive Automation?
Cognitive automation is a term that describes various ways in which AI and process automation combine their capabilities to improve business outcomes. They use their powers to take over tasks that require manual labor to be accomplished. 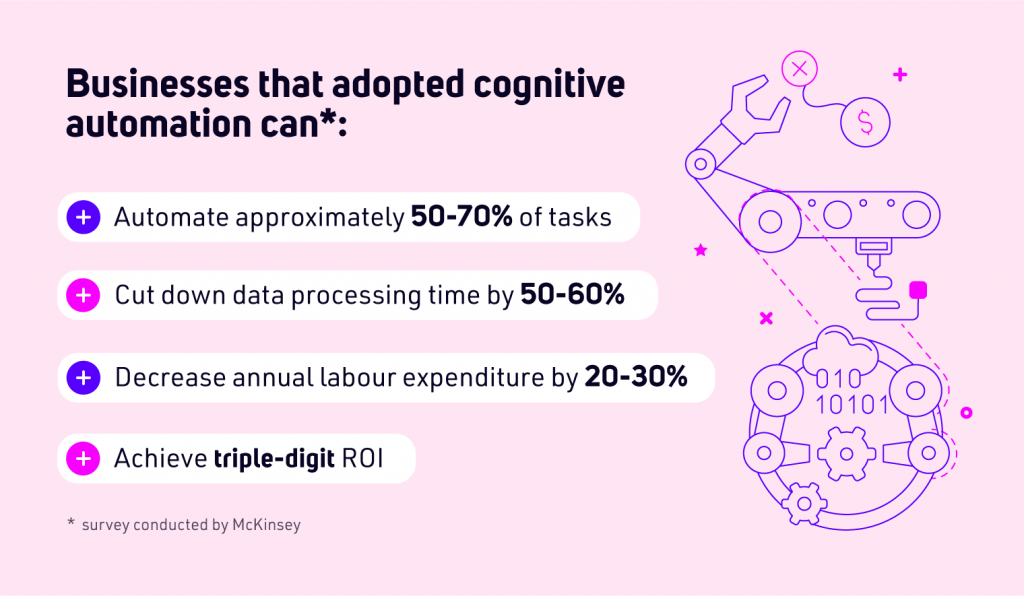
The main advantages of cognitive automation include:
- Turning unstructured data gathered from documents, customer interactions, voice and machine vision into business workflows.
- Streamlining IT service management tasks to identify the issue quicker and automate a proper response.
- Bridging the gaps between RPA bots, low-code applications and programming interface integration tools.
- Automating decision-making processes to reduce manual work and speed up business processes that human decisions can diminish.
Improving customer experience by combining RPA bots, conversational AI chatbots and virtual assistants.
Cognitive Automation vs RPA – choose the better option for your business
RPA and cognitive automation are sometimes used interchangeably. While they are both important automation technologies, there are some differences between them, including the types of data they work with and how they are programmed. In our previous article, we’ve already mentioned a few differences between RPA and cognitive automation, but we want to expand this interesting topic a little more. So, let’s compare cognitive automation with RPA.
Unstructured vs structured data
As RPA has been around for over 20 years, its technology is based on use cases with structured data, such as repetitive information entered into an ERP when processing invoices. On the other hand, cognitive automation usually works with unstructured data, including emails, videos, or voice messages. Also, it can scan an invoice to find the correct amounts to pay, identify the payee and detect inconsistencies or even fraud.
Knowing the differences can be quite important when deciding on the technology. For example, traditional RPA usually struggles with scaling or even breaks down while processing changes. Cognitive automation is more flexible and adaptable, which helps in more advanced process automation.
Long-term vs short-term ROI
RPA offers immediate ROI, while cognitive automation often takes more time to see the results. That’s because it involves learning human behavior and language to interpret and automate the data.
RPA primarily focused on manual processes and was used mainly to increase efficiency. Although it is very effective, it can’t deal with complex decision-making. On the other hand, cognitive automation unlocks many of these constraints by being able to automate and integrate across an entire value chain more fully and, in doing so, broaden the value realization that can be achieved.
Human-like thinking vs ruled-based tasks
RPA excels at automating rules-based tasks that closely follow logic. In contrast, cognitive automation is better suited to understanding insights that mimic human judgment. Therefore, it is most valuable when applied in a complex IT environment with non-standardized and unstructured data. At the same time, RPA works best in a stable environment with standardized and structured data.
Process automation is the foundation of both RPA and cognitive automation. However, cognitive automation extends the nature and diversity of the data it can interpret and the complexity of its decisions. All this happens thanks to combining optical character recognition (OCR), computer vision, natural language processing, and virtual agents. These skills enable more complex decision-making reasoning and predictive analytics.
Complex actions vs repetitive tasks
RPA is best for straight-through processing activities that follow a more deterministic logic. On the other hand, cognitive automation excels at automating more complex and less rules-based tasks. RPA automates routine and repetitive tasks, usually carried out by employees relying on basic technologies. 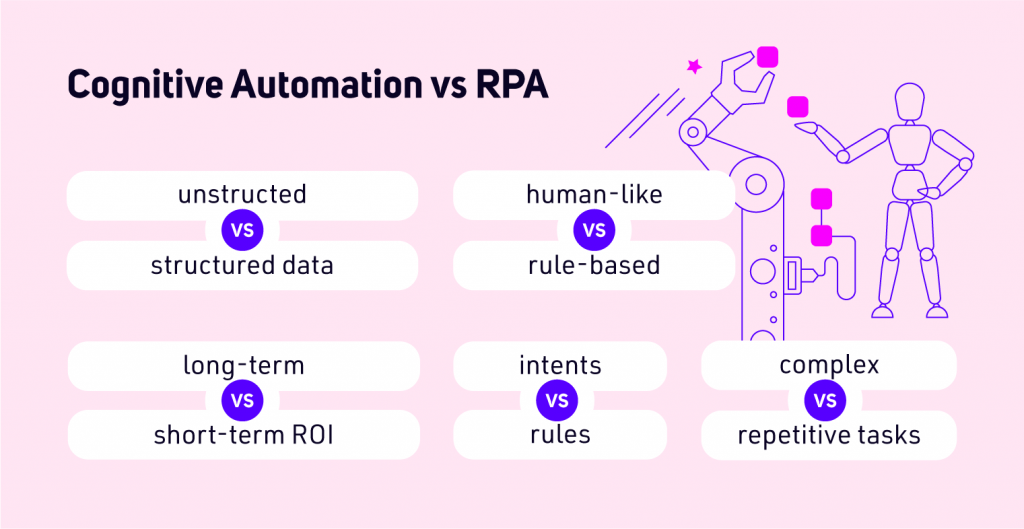
RPA performs tasks with more precision and accuracy by using software robots. But when it comes to complex data, it can be very challenging and may require human intervention. This is where cognitive automation comes in. For example, cognitive automation can use OCR to capture text from a document and NLP to understand the entities and then organize them into the workflow.
Learning from intents vs explicitly programmed
RPA can perform a specific task following rudimentary rules that are executed for as long as the surrounding system remains unchanged. Conversely, cognitive automation learns the intent of a situation using available senses to execute a task, similar to how humans learn. Then, it can use these senses to make predictions and intelligent choices.
Summary: what should you choose?
RPA is a good way to start with automating processes, and cognitive automation is a great continuum. RPA was initially used to perform repetitive tasks with greater precision and accuracy. It has helped companies reduce back-office costs and increase employees productivity. However, more complex tasks require context, judgment and learning ability. Cognitive automation can use AI techniques, taking process automation to the next level.
How can Cognitive Automation help your business?
We gathered a few use cases from various sectors to prove that cognitive automation is really useful in automating business processes. Furthermore, they show that companies are increasingly adopting this new technology to level up the process automation.
Gathering data in the retail industry
One of the major challenges in the retail industry is harmonizing data from different stores. Cognitive automation can help improve their data collection process so they can create better analytics and AI applications. For example, a global performance management company that provides a comprehensive understanding of what consumers watch and buy faced challenges in product categorization involving harmonizing product information from global HQ to local shops.
The company implemented a cognitive automation application based on established global standards to automate categorization at the local level. The incoming data from retailers and vendors, which consisted of multiple formats such as text and images, are now processed using cognitive automation capabilities. The local datasets are matched with global standards to create a new set of clean, structured data. This approach led to 98.5% accuracy in product categorization and reduced manual efforts by 80%.
Automating accounting processes
Accounting departments can also benefit from cognitive automation, for example, by automating the invoicing process with the help of the software bot. It can mimic the human role by opening the email, receiving invoice data from an email or PDF file, and entering it into the company’s accounting system. While the bot handles this manual task, the accounting team can spend more time analyzing vendor payments and identifying areas to improve the company’s cash flow.
Intelligent document processing
Processing documents is a task seen in various sectors. Usually, they need to be manually processed one by one. Employees must retype the text or use standalone optical character recognition tools to copy and paste information from a PDF file into the system. Cognitive automation uses innovative technologies like OCR to do it automatically, so the employee can supervise and make decisions based on extracted data. 
Understanding unstructured data makes cognitive automation a great tool to handle some of the most mission-critical business functions efficiently and without human error. For example, in the healthcare sector, where employees deal with millions of documents, cognitive automation could help them take better care of people.
Employee onboarding
Another example of a complex, manual process that requires a lot of human work is employee onboarding. All the steps needed to introduce employees to their company can be streamlined with cognitive automation. Bots can help by taking care of many required tasks quickly, efficiently, predictable and error-freely. This includes automatically creating logins for new employees, enrolling them on training sessions based on their departments, or scheduling meetings with their managers – all during employees’ first day at the desk.
Understanding business processes
Cognitive automation also can help in automatically inventorying complex business processes. Automating complex processes requires a clear understanding of every step to completing a task. Whether these are accounting processes, hospital patient care, or ordering supplies, developing automated process discovery tools can help.
The Cognitive Hand – a solution for process automation
We created a solution that works best for process automation using cognitive automation capabilities. The Cognitive Hand is an application developed by 4Semantics, a company that is a part of TUATARA Group, that uses NLP mechanisms to understand documents and observe how users work with business applications.
The Cognitive Hand works as an installed browser plug-in. It opens from the side panel to present its main analytical skills, such as:
- Document analysis and classification
- Extracting data from documents
- Suggesting the data that should be filled in
- Helping users to make a decision
- Filling out a form or an application
- Formulating the reply to the client.
If you want to know more about The Cognitive Hand and how it can help automate business processes, visit the product’s website or contact us.